- India is the world’s third largest producer and third largest consumer of electricity.
- The national electric grid in India has an installed capacity of 375.32 GW as of 31 December 2020.
- Renewable power plants, which also include large hydroelectric plants, constitute 36.17% of India’s total installed capacity.
- During the 2019-20 fiscal year, the gross electricity generated by utilities in India was 1,383.5 TWh and the total electricity generation (utilities and non utilities) in the country was 1,598 TWh.
- The gross electricity consumption in 2019-20 was 1,208 kWh per capita.
- In 2015-16, electric energy consumption in agriculture was recorded as being the highest (17.89%) worldwide.
- The per capita electricity consumption is low compared to most other countries despite India having a low electricity tariff.
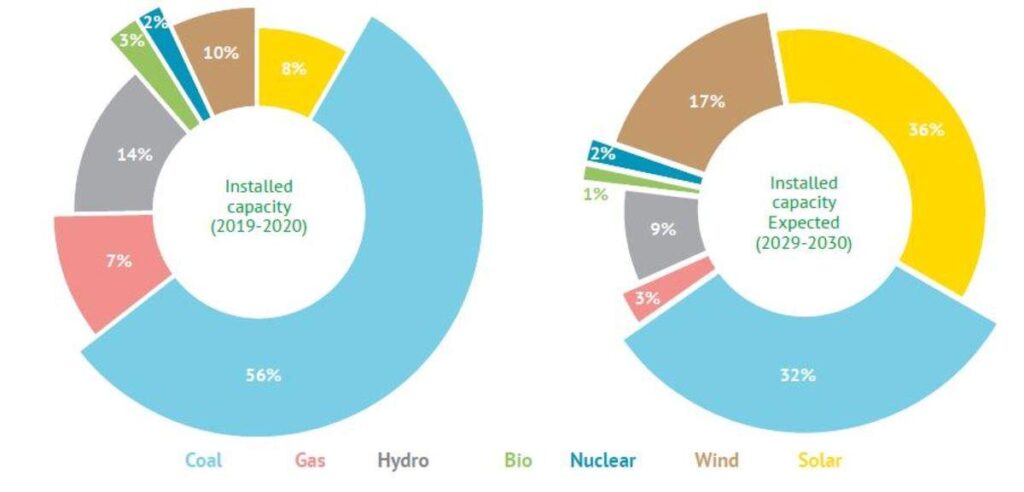
Installed Capacity of Electricity in India
As per the Central Electricity Authority (CEA) estimates, by 2029-30 the share of renewable energy generation would increase from 18 per cent to 44 per cent while that of thermal is expected to reduce from 78 per cent to 52 per cent. The projected installed capacity in year 2029-30 is around 832 GW and would comprise of 291 GW from thermal, 17 GW from Nuclear, 523 GW from Renewable energy (including 73 GW from Hydro). This shift would to be driven by the falling cost of solar panels and battery storage systems.
History
- The first demonstration of electric light in Calcutta (now Kolkata) was conducted on 24 July 1879 by P.W. Fleury & Co.
- On 7 January 1897, Kilburn & Co secured the Calcutta electric lighting license as agents of the Indian Electric Co, which was registered in London on 15 January 1897.
- A month later, the company was renamed the Calcutta Electric Supply Corporation. The control of the company was transferred from London to Calcutta only in 1970.
- The introduction of electricity in Calcutta was a success, and power was next introduced in Bombay (now Mumbai).
- The first electric lighting demonstration in Mumbai was in 1882 at Crawford Market and the Bombay Electric Supply & Tramways Company (BEST) set up a generating station in 1905 to provide electricity for the tramway.
- The first hydroelectric installation in India was installed near a tea estate at Sidrapong for the Darjeeling Municipality in 1897.
- The first electric street light in Asia was lit on 5 August 1905 in Bangalore.
- The first electric train in the country ran on the Harbour Line between Bombay’s Victoria Terminusand Kurla on 3 February 1925.
- On 18 August 2015, Cochin International Airport became the world’s first fully solar powered airport with the inauguration of a dedicated solar plant.
- India began using grid management on a regional basis in the 1960s. Individual State grids were interconnected to form 5 regional grids covering mainland India, the Northern, Eastern, Western, North Eastern and Southern Grids. These regional links were established to enable transmission of surplus electricity between states in each region.