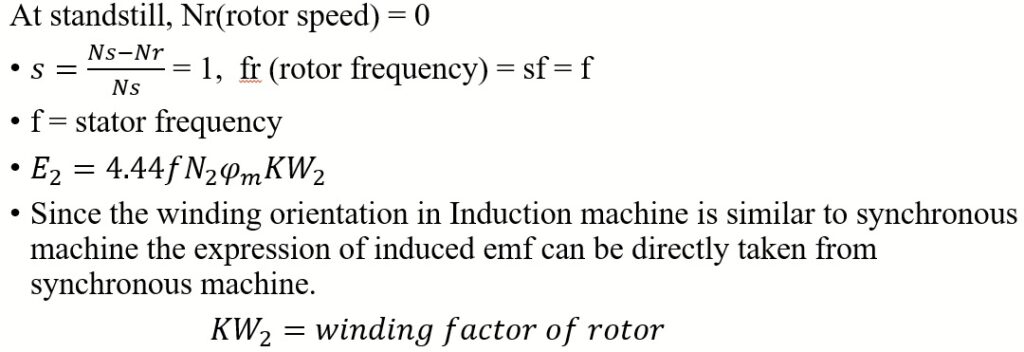

- Under running condition the rotor frequency is scaled by a factor of “s” due to which all the parameters that are directly proportional to frequency such as emf and reactance also scaled by a factor of “s”.
- We considered the resistance to be independent of the frequency hence the rotor resistance remain same under standstill as well as running condition.
- Rotor Impedance
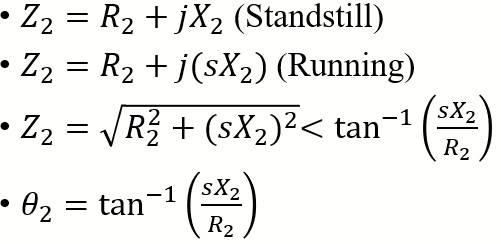
- Since the rotor conductors are always short circuited the rotor circuited only contain induced emf, rotor resistance, leakage reactance.
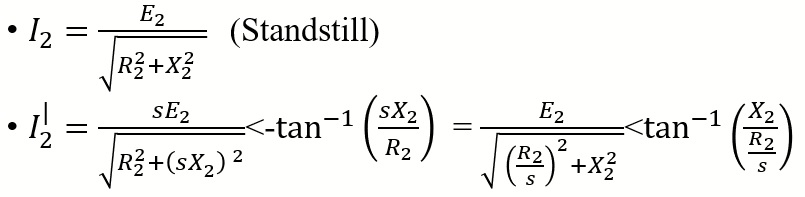
- If slip is taken common from numerator and denominator then emf and reactance become independent of the slip and the rotor resistance becomes a function of slip.
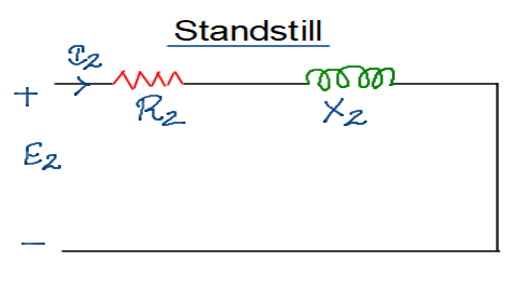
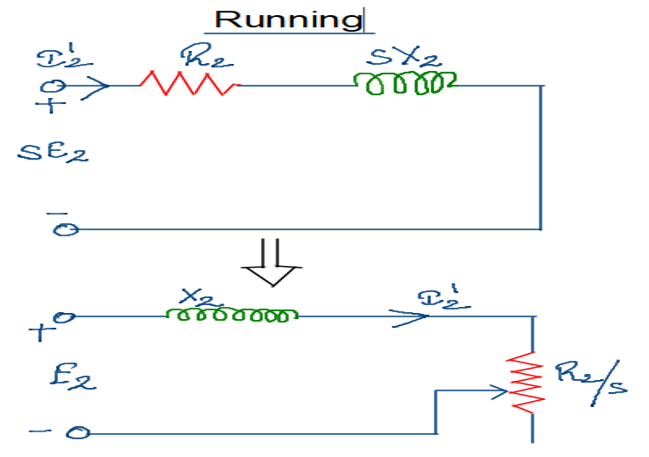
- Resistance is shown as a variable in equivalent circuit because as the speed of the motor vary the slip also varies by which the effective rotor resistance changes.
Per Phase power Input from stator to rotor
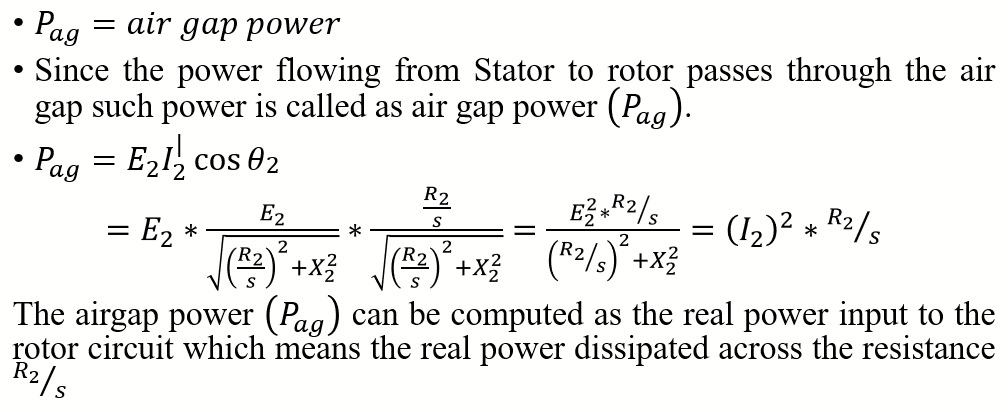
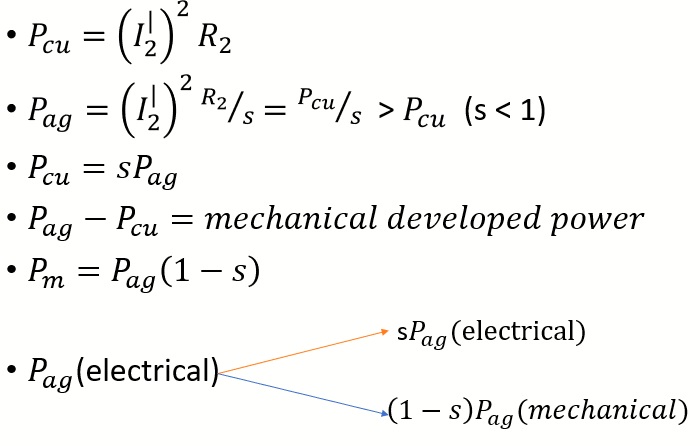
Rotor Copper Loss( 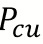 )
)

The next time I read a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as much as this one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read, but I actually thought youd have something interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you could fix if you werent too busy looking for attention.