Induction machine is a singly excited AC machine in which supply is only connected at 1 winding and other winding receives energy from first winding by means of mutual induction.
The stator of induction machine is excited by means of 3 phase AC supply and the rotor receives its energy from the stator through the air gap by the process of mutual induction.
3 phase AC supply on the stator produces a rotating magnetic field which cuts the rotor conductor and induces an EMF in the rotor causing a current to flows from stator to rotor by means of mutual EMF.
If the rotor rotates at a speed less then synchronous speed (Ns) then the machine works as a motor and if the rotor rotates at a speed greater then synchronous speed (Ns) by means of prime mover then machine works as generator.
Since the induction machine can never rotate at Ns it is also called as asynchronous machine
COMPARISON OF INDUCTION MACHINE AND TRANSFORMERS
Induction Motor
Transformer
Singly excited machine
Singly excited machine
Stator and Rotor
Primary and Secondary
Principle of mutual Induction
Principle of mutual Induction
Electromechanical Energy Conversion
no energy conversion
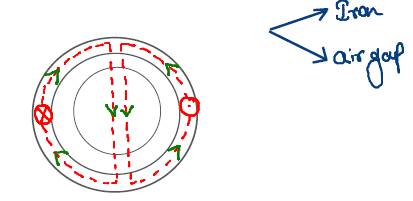
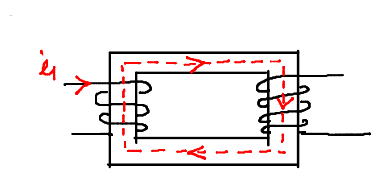
Composite magnetic circuit
Only iron is present in flux path
Induction Motor
Transformer
The reluctance of the flux path is high due to airgap between Stator and rotor.
The reluctance of the flux path is low because there is no air gap between primary and
secondary
Due to high reluctance the magnetizing current required for same amount of flux is higher in
Induction machine
Since reluctance is low less magnetizing current is drawn from the supply
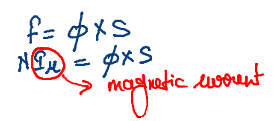
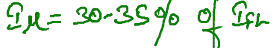
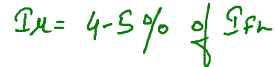
Induction machine variable frquency device
Transformer constant frequency device
Waiting for next blog sir
working on it….coming soon